| Telangiectasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Spider veins, angioectasias | |
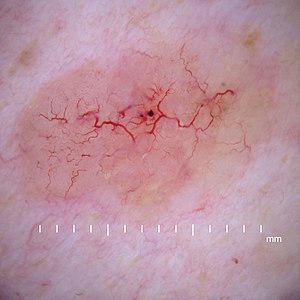 | |
| Telangiectasia as seen in a basal-cell carcinoma | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Telangiectasias, also known as spider veins, are small dilated blood vessels[1] that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, measuring between 0.5 and 1 millimeter in diameter.[2] These dilated blood vessels can develop anywhere on the body but are commonly seen on the face around the nose, cheeks and chin. Dilated blood vessels can also develop on the legs, although when they occur on the legs, they often have underlying venous reflux or "hidden varicose veins" (see Venous hypertension section below). When found on the legs, they are found specifically on the upper thigh, below the knee joint and around the ankles.
Many people who suffer with spider veins seek the assistance of physicians who specialize in vein care or peripheral vascular disease. These physicians are called vascular surgeons or phlebologists. More recently, interventional radiologists have started treating venous problems.
Some telangiectasias are due to developmental abnormalities that can closely mimic the behaviour of benign vascular neoplasms. They may be composed of abnormal aggregations of arterioles, capillaries or venules. Because telangiectasias are vascular lesions, they blanch when tested with diascopy.
Telangiectasias, aside from presenting in many other conditions, are one of the features of the acronymically named CREST syndrome, a form of systemic scleroderma. The syndrome recognises the significantly co-presenting symptoms of calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly and telangiectasia.
Causes[edit | edit source]
The causes of telangiectasia can be divided into congenital and acquired factors.
Genetic[edit | edit source]
Goldman states that "numerous inherited or congenital conditions display cutaneous telangiectasia".[2] These include:
- Bloom syndrome (homozygous null mutation in BLM DNA repair enzyme. similar mechanism and etiology to ataxia telangiectasia)
- Naevus flammeus (port-wine stain)
- Klippel–Trenaunay syndrome
- Maffucci syndrome (multiple enchondromas and hemangiomas)
- Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler–Weber–Rendu syndrome)
- Ataxia–telangiectasia
- Sturge–Weber syndrome, a nevus formation in the skin supplied by the trigeminal nerve and associated with facial port-wine stains, glaucoma, meningeal angiomas and intellectual disabilities
- Hypotrichosis–lymphedema–telangiectasia syndrome, caused by mutation in transcription factor SOX18[3]
Venous hypertension[edit | edit source]
In the past, it was believed that leg varicose veins or telangectasia were caused by high venous pressure or "venous hypertension". However it is now understood that venous reflux disease is usually the cause of these problems.[4][full citation needed]
Telangiectasia in the legs is often related to the presence of venous reflux within underlying varicose veins. Flow abnormalities within the medium-sized veins of the leg (reticular veins) can also lead to the development of telangiectasia. Factors that predispose to the development of varicose and telangiectatic leg veins include
- Age
- Gender: It used to be thought that females were affected far more than males. However, research has shown 79% of adult males and 88% of adult females have leg telangectasia (spider veins).[5]
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy is a key factor contributing to the formation of varicose and spider veins. The most important factor is circulating hormones that weaken vein walls. There's also a significant increase in the blood volume during pregnancy, which tends to distend veins, causing valve dysfunction which leads to blood pooling in the veins. Moreover, later in pregnancy, the enlarged uterus can compress veins, causing higher vein pressure leading to dilated veins. Varicose veins that form during pregnancy may spontaneously improve or even disappear a few months after delivery.[6]
- Lifestyle/occupation: Those who are involved with prolonged sitting or standing in their daily activities have an increased risk of developing varicose veins. The weight of the blood continuously pressing against the closed valves causes them to fail, leading to vein distention.[7]
Other acquired causes[edit | edit source]
Acquired telangiectasia, not related to other venous abnormalities, for example on the face and trunk, can be caused by factors such as
- Cushing's syndrome
- Acne rosacea
- Blepharitis[8]
- Environmental damage such as that caused by sun[9] or cold exposure
- Age[9]
- Trauma to skin such as contusions or surgical incisions.
- Radiation exposure such as that experienced during radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer, e.g., radiation proctitis
- Chemotherapy
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Limited systemic sclerosis/scleroderma (a Scleroderma sub-type)
- Chronic treatment with topical corticosteroids may lead to telangiectasia.[10]
- Spider angiomas are a radial array of tiny arterioles that commonly occur in pregnant women and in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and are associated with palmar erythema. In men, they are related to high estrogen levels secondary to liver disease.
- Tempi syndrome
- Tobacco smoking[9]
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Before any treatment of leg telangectasia (spider veins) is considered, it is essential to have duplex ultrasonography, the test that has replaced Doppler ultrasound. The reason for this is that there is a clear association between leg telangectasia (spider veins) and underlying venous reflux.[11] Research has shown that 88 to 89% of women with telangectasia (spider veins) have refluxing reticular veins close,[12] and 15% have incompetent perforator veins nearby.[13] As such, it is essential to both find and treat underlying venous reflux before considering any treatment at all.
Sclerotherapy is the "gold standard" and is preferred over laser for eliminating telangiectasiae and smaller varicose leg veins.[14] A sclerosant medication is injected into the diseased vein so it hardens and eventually shrinks away. Recent evidence with foam sclerotherapy shows that the foam containing the irritating sclerosant quickly appears in the patient's heart and lungs, and then in some cases travels through a patent foramen ovale to the brain.[15] This has led to concerns about the safety of sclerotherapy for telangectasias and spider veins.
In some cases stroke and transient ischemic attacks have occurred after sclerotherapy.[16] Varicose veins and reticular veins are often treated before treating telangiectasia, although treatment of these larger veins in advance of sclerotherapy for telangiectasia may not guarantee better results.[17][18][19] Varicose veins can be treated with foam sclerotherapy, endovenous laser treatment, radiofrequency ablation, or open surgery. The biggest risk, however, seems to occur with sclerotherapy, especially in terms of systemic risk of DVT, pulmonary embolism, and stroke.[20]
Other issues which arise with the use of sclerotherapy to treat spider veins are staining, shadowing, telangetatic matting, and ulceration. In addition, incompleteness of therapy is common, requiring multiple treatment sessions.[21]
Telangiectasias on the face are often treated with a laser. Laser therapy uses a light beam that is pulsed onto the veins in order to seal them off, causing them to dissolve. These light-based treatments require adequate heating of the veins. These treatments can result in the destruction of sweat glands, and the risk increases with the number of treatments.[citation needed]
Additional images[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ "telangiectasia" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Goldman, Mitchel P (1995). Sclerotherapy treatment of varicose and telangiectatic leg veins (2nd ed.). St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 0-8151-4011-8.[page needed]
- ↑ Irrthum, Alexandre; Devriendt, Koenraad; Chitayat, David; Matthijs, Gert; Glade, Conrad; Steijlen, Peter M.; Fryns, Jean-Pierre; Van Steensel, Maurice A. M.; Vikkula, Miikka (2003). "Mutations in the Transcription Factor Gene SOX18 Underlie Recessive and Dominant Forms of Hypotrichosis-Lymphedema-Telangiectasia". The American Journal of Human Genetics. 72 (6): 1470–8. doi:10.1086/375614. PMC 1180307. PMID 12740761.
- ↑ Whiteley (2011). "Understanding Venous Reflux – the cause of varicose veins and venous leg ulcers". Archived from the original on 2017-10-25. Retrieved 2020-12-19.
- ↑ Ruckley, C.V.; Evans, C.J.; Allan, P.L.; Lee, A.J.; Fowkes, F.G.R. (2008). "Telangiectasia in the Edinburgh Vein Study: Epidemiology and Association with Trunk Varices and Symptoms". European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 36 (6): 719–24. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2008.08.012. PMID 18848475.
- ↑ Brotman O'Neill, Alissa (27 September 2019). "Pregnancy and Varicose Veins". Princeton Vascular. Archived from the original on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- ↑ "Varicose veins - Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Archived from the original on 2020-08-09. Retrieved 2020-08-11.
- ↑ Lindsley, Kristina; Matsumura, Sueko; Hatef, Elham; Akpek, Esen K (2012). "Interventions for chronic blepharitis". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 5 (5): CD005556. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005556.pub2. PMC 4270370. PMID 22592706.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Kennedy, Cornelis; Bastiaens, Maarten T.; Willemze, Rein; Bouwes Bavinck, Jan N.; Bajdik, Chris D.; Westendorp, Rudi G.J. (April 2003). "Effect of Smoking and Sun on the Aging Skin". Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 120 (4): 548–554. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12092.x. PMID 12648216.
- ↑ Johnson, B. A.; Nunley, J. R. (2000). "Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis". American Family Physician. 61 (9): 2703–10, 2713–4. PMID 10821151. Archived from the original on 2010-07-06. Retrieved 2020-12-19.
- ↑ Ruckley, C. V.; Allan, P. L.; Evans, C. J.; Lee, A. J.; Fowkes, F. G. R. (2011). "Telangiectasia and venous reflux in the Edinburgh Vein Study". Phlebology. 27 (6): 297–302. doi:10.1258/phleb.2011.011007. PMID 22106449.
- ↑ Weiss, Robert A.; Weiss, Margaret A. (1993). "Doppler Ultrasound Findings in Reticular Veins of the Thigh Subdermic Lateral Venous System and Implications for Sclerotherapy". The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology. 19 (10): 947–51. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.1993.tb00983.x. PMID 8408914.
- ↑ Somjen, George M.; Ziegenbein, Robert; Johnston, Andrew H.; Royle, John P. (1993). "Anatomical Examination of Leg Telangiectases with Duplex Scanning". The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology. 19 (10): 940–5. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.1993.tb00982.x. PMID 8408913.
- ↑ Sadick N, Sorhaindo L (2007). "16. Laser Treatment of Telangiectatic and Reticular Veins". In Bergan, John J. (ed.). The Vein Book. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press. p. 157. ISBN 978-0-12-369515-4.
- ↑ Ceulen, Roeland P.M.; Sommer, Anja; Vernooy, Kevin (2008). "Microembolism during Foam Sclerotherapy of Varicose Veins". New England Journal of Medicine. 358 (14): 1525–6. doi:10.1056/NEJMc0707265. PMID 18385510.
- ↑ Forlee, Martin V.; Grouden, Maria; Moore, Dermot J.; Shanik, Gregor (2006). "Stroke after varicose vein foam injection sclerotherapy". Journal of Vascular Surgery. 43 (1): 162–4. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2005.09.032. PMID 16414404.
- ↑ Duffy, David M. (2012). "Sclerotherapy for Telangiectasia – The impact of small changes in vessel size on treatment outcomes" (PDF). Cosmetic Dermatology. 25 (3): 126–33. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-12-15.
- ↑ Treatment of Leg Veins. Procedures in Cosmetic Dermatology Series. Editors Murad Alam, Sirunya Silapunt. Second Edition Saunders Elsevier Inc. 2011[page needed]
- ↑ Schuller-Petrovic, S.; Pavlovic, M. D.; Schuller, S.; Schuller-Lukic, B.; Adamic, M. (2012). "Telangiectasias resistant to sclerotherapy are commonly connected to a perforating vessel". Phlebology. 28 (6): 320–3. doi:10.1258/phleb.2012.012019. PMID 22865418.
- ↑ "Varicose Veins Symptoms Available Treatments and Cost to Fix | CMW". Complete Medical Wellness. 2020-07-27. Archived from the original on 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-08-11.
- ↑ Goldman, Mitchel P.; Bennett, Richard G. (1987-08-01). "Treatment of telangiectasia: A review". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 17 (2): 167–182. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70187-x. ISSN 0190-9622. PMID 3305603.
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)