 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50%(suppository) 64-77%(oral) |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 18-26 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
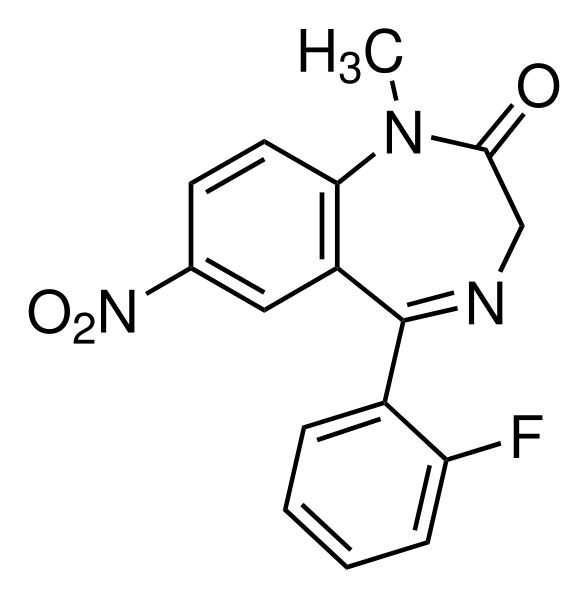
| Formula | C16H12FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 313.3 |
Overview[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam (Template:IPA2; is marketed by Roche under the trade name Rohypnol. It is a powerful hypnotic drug that is a benzodiazepine derivative. It has powerful hypnotic, sedative, anxiolytic, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties.
Flunitrazepam is commonly prescribed for the treatment of insomnia. Insomnia can be described as a difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakening, early awakenings or a combination of both. Flunitrazepam is a short-intermediate acting benzodiazepine and is sometimes used in patients who have difficulty in maintaining sleep. Intermediate half life benzodiazepines are also useful for patients with difficulty in maintaining sleep eg loprazolam, lormetazepam, temazepam and may be preferable to long half life benzodiazepines which typically cause next day sedation and impairments. Hypnotics should only be used on a short term basis or in those with chronic insomnia on an occasional basis.[1]
The drug is sometimes used as a date rape drug (commonly referred to in street slang as a "roofie").
History[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam was first synthesized in the early 1970s by Roche and was used in hospitals when deep sedation was needed. It first entered the commercial market in Europe in 1975, and in the 1980s it began to be available in other countries. It first appeared in the U.S. in the early 1990s. It originally came in 1 mg, 2 mg, and 5 mg doses, but due to its potency and potential for abuse the higher doses were soon taken off the market. It is now only available in 1 mg.
Pharmacology[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam is classed as a nitrobenzodiazepine. Other nitrobenzodiazepines include nitrazepam and clonazepam.[2] Flunitrazepam is lipophilic and is metabolised hepatically via oxidative pathways. The main pharmacological effects of flunitrazepam are the enhancement of GABA at the GABAA receptor.[3] Like other benzodiazepines, flunitrazepam's pharmacological effects include sedation, muscle relaxation, reduction in anxiety, and prevention of convulsions. However, flunitrazepam's effects are approximately 7 to 10 times more potent than diazepam. The effects of flunitrazepam appear approximately 15 to 20 minutes after oral administration, and last for approximately four to six hours. Some residual effects can persist up to 12 hours or more after administration. While 80% of flunitrazepam that is taken orally is absorbed, bioavailability in suppository form is closer to 50%.[4]
Flunitrazepam and other benzodiazepines may influence neurosteroid metabolism with alterations in the levels of progesterone which in turn may adversely influence the functions of the brain and reproductive system. The pharmacological actions of benzodiazepines at the GABAa receptor are similar to those of neurosteroids. Neuroactive steroids are positive allosteric modulators of the GABAa receptor, enhancing GABA function. Many benzodiazepines (diazepam, medazepam, estazolam, flunitrazepam and nitrazepam) potently inhibit the enzymes involved in the metabolism of neurosteroids. Long-term administration of benzodiazepines may influence the concentrations of endogenous neurosteroids, and thereby would modulate the emotional state. Factors which effects benzodiazepines ability to alter neurosteroid levels depend on the molecular make up of the individual benzodiazepine molecule. Presence of a substituent at N1 position of the diazepine ring and/or the chloro or nitro group at position 7 of the benzene ring contribute to potent inhibition of the isoenzymes, and in turn a bromo group at position 7 (for bromazepam) and additional substituents (3-hydroxy group for oxazepam and tetrahydroxazole ring for cloxazolam and oxazolam) decrease the inhibitory potency of benzodiazepines on neurosteroids.[5]
Flunitrazepam produces a decrease in delta activity. The effect of benzodiazepine drugs on delta however may not be mediated via benzodiazepine receptors. Delta activity is an indicator of depth of sleep within non-REM sleep. Delta activity is thought to reflect sleep quality with lower levels of delta sleep reflecting poorer quality of sleep. Thus flunitrazepam and other benzodiazepines cause a deterioration in sleep quality. Cyproheptadine may be superior to benzodiazepines in the treatment of insomnia as it enhances sleep quality based on EEG studies.[6]
Dependence[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam is a preferred benzodiazepine in chronic users of benzodiazepines with a chronic and massive drug usage.[7] Long-term use of flunitrazepam can result in psychological and physical dependence and the appearance of withdrawal symptoms when the drug is discontinued. Abrupt withdrawal may lead to a severe benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome characterised by seizures, psychosis, severe insomnia and severe anxiety.
Regular use of flunitrazepam may lead to a hypnotic drug dependence. Withdrawal symptoms typically appear when flunitrazepam dosage is reduced or the drug is discontinued. Withdrawal symptoms including rebound insomnia worse than baseline insomnia typically occur after discontinuation of flunitrazepam even after short term single nightly dose therapy.[8]
Medical uses[edit | edit source]
- In the United States, the drug has not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for medical use, and is considered to be an illegal drug.[9][10][11]
- In the United Kingdom, the drug is available only by private prescription.[12] Though Rohypnol was discontinued in 1986, Flunitrazepam use is still present in modern culture; among other uses, it is used in some hospitals to sedate patients undergoing colonoscopy.
- In Australia, prescription is restricted as a Schedule 8 medicine.[13][14] It is used primarily for the treatment of severe insomnia that has not responded to other treatments. In some states, it is also manufactured in generic form by Alphapharm under the name Hypnodorm. As a Schedule 8 medicine, it is illegal to have this drug in possession without an authority prescription from a registered doctor.
- In South Africa, Rohypnol is classified as a schedule 6 drug.[15] It is available by prescription only, and restricted to 1 mg doses. Travelers from South Africa to the United States are limited to a 30-day supply. The drug must be declared to US Customs upon arrival. If a valid prescription cannot be produced, the drug may be subject to Customs search and seizure, and the traveler may face criminal charges or deportation.
- Prescribing of hypnotics in Norway is quite restrictive with only 3 hypnotics which are prescribable, nitrazepam and flunitrazepam and zopiclone.[16] In Norway, the brand Rohypnol has been withdrawn from market because of its reputation, but the drug is still available under the brand-name Flunipam.
- In Sweden, the brand Rohypnol has been withdrawn from the domestic market. Instead it is available under the generic name Flunitrazepam.
- In Mexico, Rohypnol is approved for medical use,[11] however there have been many cases of trafficking of Rohypnol to the United States and other developed nations, most of it originating from Mexico.[17]
- In Germany, flunitrazepam is available as the Roche-Brand Rohypnol 1 mg Film-Coated Tablets and several generic 1 mg tablets (e.g. Fluninoc, Flunitrazepam ratiopharm, Flunitrazepam neuraxpharm). The prescription of flunitrazepam as a hypnotic is generally tended to be for short-term treatment of severe insomnias, that are not responsive to other hypnotics (though some physicians prescribe this preparate as the ultimate high-potency hypnotic in severe cases of insomnia even as first-line option), especially in inpatients. It is considered to be one of the most potent benzodiazepine hypnotic (rather on effect than on dose basis; i.e., its hypnotic effect is being considered to be one of the most strongly pronounced of all benzodiazepine hypnotics available). Abuse of flunitrazepam among drug addicts is considerable and any possession of flunitrazepam without a valid prescription is illegal.
Side effects[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam is considered to be one of the most addictive of the benzodiazepines, along with clonazepam, lorazepam, alprazolam, and particularily, temazepam, nitrazepam, and nimetazepam. Its use causes several notable side effects, including:
- Somnolence
- Impaired motor function
- Impaired coordination
- Impaired balance
- Dizziness
- Lack of concentration
- Slurred speech
- Anterograde amnesia
- Confusion
- Gastrointestinal disturbances, lasting 12 or more hours/Vomiting
- Respiratory depression in higher doses
Flunitrazepam impairs cognitive and psychomotor functions, affecting reaction time and driving skill. The use of this drug in combination with alcohol potentiates these side effects, and can lead to toxicity and death.
A hangover like effect occurs with flunitrazepam with impairment of mental arithmetic abilities. After disconinuation of flunitrazepam a rebound effect may occur about 4 days after stopping flunitrazepam.[18] (See benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome)
Flunitrazepam has a long half life of 18 - 26 hours and an active metabolite which has a half life of 36-200 which means flunitrazepam effects after nighttime administration persist throughout the next day.[19] Residual 'hangover' effects after nighttime administration of flunitrazepam such as sleepiness, impaired psychomotor and cognitive may persist into the next day which may impair the ability of users to drive safely and increase risks of falls and hip fractures.[20]
Special precautions[edit | edit source]
Benzodiazepines such as flunitrazepam are lipophilic and rapidly penetrate membranes and therefore rapidly crosses over into the placenta with significant uptake of the drug. Use of benzodiazepines including flunitrazepam in late pregnancy, especially high doses, may result in floppy infant syndrome.[21]
Interactions[edit | edit source]
Benzodiazepines including flunitrazepam may inhibit the glucuronidation of morphine leading to increased levels of and prolongation of the effects of morphine.[22]
Abuse potential[edit | edit source]
Despite the fact that flunitrazepam is a Schedule IV controlled substance, it is not commercially available in the United States. Currently the DEA is recommending that Rohypnol be reclassified to Schedule I.
Drug-facilitated sexual assault[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam is known to induce anterograde amnesia in sufficient doses; individuals are unable to remember certain events that they experienced while under the influence of the drug. This effect is particularly dangerous when flunitrazepam is used to aid in the commission of sexual assault; victims may not be able to clearly recall the assault, the assailant, or the events surrounding the assault.
It is difficult to estimate just how many flunitrazepam-facilitated rapes have occurred in the past. Very often, biological samples are taken from the victim at a time when the effects of the drug have already passed and only residual amounts remain in the body fluids. These residual amounts are difficult, and sometimes impossible, to detect using standard screening assays available in the United States. If flunitrazepam exposure is to be detected at all, urine samples need to be collected within 72 hours and subjected to sensitive analytical tests. The problem is compounded by the onset of amnesia after ingestion of the drug, which causes the victim to be uncertain about the facts surrounding the rape. This uncertainty may lead to critical delays or even reluctance to report the rape and provide appropriate biological samples for testing. If a person suspects that he or she is the victim of a flunitrazepam-facilitated rape, he or she should get laboratory testing for flunitrazepam as soon as possible. In recent news it has been discovered that scientists can now detect flunitrazepam and related compounds in urine at least up to 5 days after administration of a single dose of Rohypnol and up to a month in hair.[23]
It must be noted that an inability to remember events, including sexual encounters, is not conclusive evidence of having consumed a drugged drink: Drunkenness itself causes blackouts, sleepiness, and a reduction in inhibitions. Only a timely screening for flunitrazepam can demonstrate its use. It has been shown that alcohol alone is the substance used in the vast majority of cases of date-rape. A recent study conducted by doctors in the U.K. found that none of the subjects reporting spiked drinks had any traces of flunitrazepam or other medications popularly believed to be associated with rape such as GHB. The study claims that binge drinking was to blame.[24]
Drug-facilitated robbery[edit | edit source]
In the United Kingdom, the use of flunitrazepam and other "date rape" drugs has been connected to stealing from sedated victims. One expert quoted in a British tabloid estimated that up to 2,000 individuals are robbed each year after being spiked with powerful sedatives,[25] making drug-assisted robbery a more common problem than drug-assisted rape.
Criminals sometimes use flunitrazepam before committing robbery as it has a calming and anti-emotive effect. This allows the criminal to perform the robbery without becoming anxious. Flunitrazepam is also known to induce anterograde amnesia making police interrogations more difficult.[26][27][28]
In a notable flunitrazepam related case, Selina Hakki was found guilty in December 2004 of using flunitrazepam to drug wealthy men and rob them of their clothes and accessories in the UK.
Recreational drug[edit | edit source]
Although flunitrazepam has become widely known in USA for its use as a date-rape drug, it is used more frequently as a recreational drug. It is used by high school and college students, rave party attendees, and heroin and cocaine users (who call a dose of flunitrazepam a "roofie") for recreational purposes, including:
- To produce profound intoxication (Kurt Cobain overdosed on a mixture of flunitrazepam and champagne several weeks before his death)
- To boost the high produced by heroin, or ease the anxiety and/or sleeplessness of withdrawal
- To counteract the side effects of stimulants (e.g. insomnia, paranoia, jitteriness)
- To "soften" the so-called "crash" which follows heavy usage of stimulants, such as cocaine or methamphetamine
Flunitrazepam is usually consumed orally, and is often combined with alcohol. It is also occasionally insufflated (i.e. tablets are crushed into powder and snorted). In some European countries, there was an alcohol solution of flunitrazepam (Darkene), taken by injection, with very strong effects.
Benzodiazepines, including diazepam, nitrazepam, oxazepam and flunitrazepam account for the largest volume of forged drug prescriptions in Sweden, a total of 52% of drug forgeries being for benzodiazepines, suggesting benzodiazepines are a major prescription drug class of abuse. Nitrazepam and flunitrazepam accounted for the vast majority of forged prescriptions.[29]
Flunitrazepam and other sedative hypnotic drugs are detected frequently in cases of people suspected of driving under the influence of drugs. Other benzodiazepines and zolpidem and zopiclone are also found in high numbers of suspected drugged drivers. Many drivers have blood levels far exceeding the therapeutic dose range suggesting a high degree of abuse potential for benzodiazepines and zolpidem and zopiclone.[30]
Overdose[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam is a drug which is very frequently involved in drug intoxication, including overdose.[31] Overdose of flunitrazepam may result in excessive sedation, impairment of balance and speech. This may progress in severe overdoses to respiratory depression or coma and possibly death. The risk of overdose is increased if flunitrazepam is taken in combination with alcohol, opiates or other CNS depressants. Flunitrazepam overdose responds to the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist flumazenil.
Benzodiazepines were implicated in 39% of suicides by drug poisoning in Sweden, with nitrazepam and flunitrazepam accounting for 90% of benzodiazepine implicated suicides, in the elderly over a period of 2 decades. In three quarters of cases death was due to drowning, typically in the bath. Benzodiazepines were the predominant drug class used in suicides in this review of Swedish death certificates with 72% of benzodiazepine overdoses showing that benzodiazepines were the sole drug used in deaths by overdose. Benzodiazepines and in particular nitrazepam and flunitrazepam should therefore be prescribed with caution in the elderly.[32]It was also found that in about a third of overdose cases involving benzodiazepines, benzodiazepines were the sole cause of death.[33]
In a retrospective study of deaths, when benzodiazepines were implicated in the deaths, the benzodiazepines flunitrazepam, and nitrazepam were the most common benzodiazepines involved. Benzodiazepines were a factor in all deaths caused by drug addiction in the study. Nitrazepam and flunitrazepam were significantly more commonly implicated in suicide related deaths than natural deaths. In four of the cases benzodiazepines alone were the only cause of death. It was concluded that flunitrazepam and nitrazepam were significantly more toxic than other benzodiazepines.[34]
Legal status[edit | edit source]
Flunitrazepam is currently a Schedule III drug under the international Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971;[35] in the United States, it is on Schedule IV
According to FDA Associate Director for Domestic and International Drug Control Nicholas Reuter:[36]
- Flunitrazepam was "temporarily controlled in Schedule IV pursuant to a treaty obligation under the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances. At the time flunitrazepam was placed temporarily in Schedule IV . . . there was no evidence of abuse or trafficking of the drug in the United States."
Rohypnol is currently under consideration to be rescheduled to Schedule I, and is already considered such in the States of Florida, Idaho, Minnesota, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, and Pennsylvania.
Template:UnitedStatesCode and Template:UnitedStatesCode provide for stiff prison terms for the possession of flunitrazepam; penalties for use or distribution include life in prison, should death or serious injury occur.
In Australia, flunitrazepam is a schedule 8 drug, along with amphetamines and narcotic analgesics. All other benzodiazepines (except Temazepam) are schedule 4 drugs. Unauthorized possession of certain quantities of the drug is punishable by criminal sanctions in New South Wales under Schedule 1 of the Drug Misuse and Trafficking Act 1985.
On January the 1st 2003 flunitrazepam was moved up one level in the schedule of controlled drugs and on August 1st 2004 the manufacturer Roche removed Rohypnol from the market.[37]
Street terms[edit | edit source]
Street names for Rohypnol include rophy, rufflels, roofies, ruffies, ruff up, rib, roach 2, R2, R2-Do-U, roche, rope, ropies, circles, circes, forget it, forget-me-pill, forget-me-now, Baptist Communion, and Mexican Valium.[38]
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- Inchem - Retrieved 2007-2-27
Footnotes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Rickels K. (1986). "The clinical use of hypnotics: indications for use and the need for a variety of hypnotics". Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 332: 132–41. PMID 2883820.
- ↑ Robertson MD (1995). "Postmortem drug metabolism by bacteria". J Forensic Sci. 40 (3): 382–6. PMID 7782744. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Oelschläger H. (4). "[Chemical and pharmacologic aspects of benzodiazepines]". Schweiz Rundsch Med Prax. 78 (27–28): 766–72. PMID 2570451. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ Cano J. P. (1977). "Bioavailability from various galenic formulations of flunitrazepam". Arzneimittelforschung. 27 (12): 2383-8. rohypnol. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Usami N (2002). "Substrate specificity of human 3(20)alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase for neurosteroids and its inhibition by benzodiazepines" (pdf). Biol Pharm Bull. 25 (4): 441–5. PMID 11995921. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Tokunaga S (2007). "Effects of some H1-antagonists on the sleep-wake cycle in sleep-disturbed rats" (pdf). J Pharmacol Sci. 103 (2): 201–6. PMID 17287588. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Veje JO (21). "[Prescription of tranquilizers and hypnotics in the municipality of Holbaek]". Ugeskr Laeger. 151 (34): 2134–6. PMID 2773144. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ Kales A (20). "Rebound insomnia. A potential hazard following withdrawal of certain benzodiazepines". JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association. 241 (16): 1692–5. PMID 430730. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ [1]
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Women's Health.gov: Date Rape Drugs
- ↑ "UK Rohypnol: The date rape drug". BBC News Online. Thursday, May 20, 1999. Retrieved 2006-03-13. Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ "Authorisation to Supply or Prescribe Drugs of Addiction: Flunitrazepam". Statutory Medical Notifications. Department of Health, Government of Western Australia. 13 August 2004. Retrieved 2006-03-13. Check date values in:
|year=(help) - ↑ "Guidelines for the Prescribing of Flunitrazepam" (PDF). Pharmaceutical Services Branch. New South Wales Health. August 2000. Retrieved 2006-03-13.
- ↑ "Drug Wars - About Drugs". 11 October 2006. Check date values in:
|year=(help) - ↑ Kayed K. (30). "[Insomnia and hypnotics]". Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 115 (9): 1087–90. PMID 7725291. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ http://www.dea.gov/pubs/states/texas.html
- ↑ Hindmarch I. (1977). "A repeated dose comparison of three benzodiazepine derivative (nitrazepam, flurazepam and flunitrazepam) on subjective appraisals of sleep and measures of psychomotor performance the morning following night-time medication". Acta Psychiatr Scand. 56 (5): 373–81. PMID 22990. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ [3]
- ↑ Vermeeren A. (2004). "Residual effects of hypnotics: epidemiology and clinical implications". CNS Drugs. 18 (5): 297–328. PMID 15089115.
- ↑ Kanto JH. (1982). "Use of benzodiazepines during pregnancy, labour and lactation, with particular reference to pharmacokinetic considerations". Drugs. 23 (5): 354–80. PMID 6124415. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Pacifici GM (1986). "Metabolic interaction between morphine and various benzodiazepines". Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 58 (4): 249–52. PMID 2872767. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ [4]
- ↑ [5]
- ↑ [6]
- ↑ "Bankrånare stärkte sig med Rohypnol?". DrugNews.
- ↑ "Mijailovic var påverkad av våldsdrog". Sydsvenskan.
- ↑ "Mijailovic var påverkad av våldsdrog". Expressen.
- ↑ Bergman U (1989). "Use of prescription forgeries in a drug abuse surveillance network". Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 36 (6): 621–3. PMID 2776820. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Jones AW (2007). "Concentrations of scheduled prescription drugs in blood of impaired drivers: considerations for interpreting the results". Ther Drug Monit. 29 (2): 248–60. PMID 17417081. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Zevzikovas A (2002). "[Analysis of benzodiazepine derivative mixture by gas-liquid chromatography]". Medicina (Kaunas). 38 (3): 316–20. PMID 12474705. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Carlsten, A (2003). "The role of benzodiazepines in elderly suicides". Scand J Public Health. 31 (3): 224–8. PMID 12850977. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Drummer OH (1996). "Sudden death and benzodiazepines". Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 17 (4): 336–42. PMID 8947361. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ericsson HR (10). "[Benzodiazepine findings in autopsy material. A study shows interacting factors in fatal cases]". Läkartidningen. 90 (45): 3954–7. PMID 8231567. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ [7]
- ↑ [8]
- ↑ Bramness JG (23). "[Changes in the sale and use of flunitrazepam in Norway after 1999]". Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 126 (5): 589–90. PMID 16505866. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=, |year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ Rohypnol fact sheet at About.com Teen Advice
External links[edit | edit source]
- Drugs Factfile on Rohypnol all you need to know
- Molecule of the Month
- Statement on "Date Rape" Drugs by Nicholas Reuter, M.P.H., Mar. 11, 1999.
- Club Drugs - Fact Sheet by Drug Policy Information Clearing House, United States.
cs:Flunitrazepam da:Flunitrazepam de:Flunitrazepam gl:Flunitrazepam it:Rohypnol hu:Flunitrazepam nl:Flunitrazepam no:Flunitrazepam fi:Flunitratsepaami sv:Flunitrazepam Template:Jb1 Template:WH Template:WikiDoc Sources
