1 Definition[edit | edit source]
- For some, ubiquitous learning (or u-learning) is equivalent to some form of simple mobile learning, e.g. that learning environments can be accessed in various contexts and situations.
However, DSchneider thinks that u-learning R&D programs more ambitious. E.g. according to Ogata & Yano (2003) based on Chen (2002) and Curtis (2002), the main characteristics of ubiquitous learning are the following:
- Permanency: Learners never lose their work unless it is purposefully deleted. In addition, all the learning processes are recorded continuously everyday.
- Accessibility: Learners have access to their documents, data, or videos from anywhere. That information is provided based on their requests. Therefore, the learning involved is self-directed.
- Immediacy: Wherever learners are, they can get any information immediately. Thus, learners can solve problems quickly. Otherwise, the learner can record the questions and look for the answer later.
- Interactivity: Learners can interact with experts, teachers, or peers in the form of synchronies or asynchronous communication. Hence, the experts are more reachable and the knowledge becomes more available.
- Situating of instructional activities: The learning could be embedded in our daily life. The problems encountered as well as the knowledge required are all presented in their natural and authentic forms. This helps learners notice the features of problem situations that make particular actions relevant.
- Adaptability: Learners can get the right information at the right place with the right way. [ Additional feature, from [1] ]
Moreover, ubiquitous learning can be empowered by Computer Supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL) environments that focus on the socio-cognitive process of social knowledge construction and sharing.
There are also trends to incorporate [connected objects] other than computers, PDAs or phones.See also: ubiquitous computing
Yeonjeong Park (2011) illustrates the conceptual shifts from e-learning to m-learning then to u-learning with the following figure:
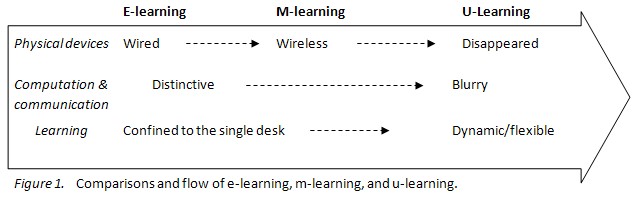
Source: Park, Y. (2011). A Pedagogical Framework for Mobile Learning: Categorizing Educational Applications of Mobile Technologies into Four Types, IRRODL, 12(2).
2 Links[edit | edit source]
- Research on Ubiquitous CSCL, Project lead by Hiroaki Ogata.
2.1 Conferences[edit | edit source]
- WMTE series:
- MLearn 2006
2.2 Research consortia[edit | edit source]
3 References[edit | edit source]
- Bomsdorf, Birgit, Adaptation of Learning Spaces: Supporting Ubiquitous Learning in Higher Distance Education, Dagstuhl Seminar Proceedings 05181, Mobile Computing and Ambient Intelligence: The Challenge of Multimedia, Abstract/PDF
- Chen, Y.S., Kao, T.C., Sheu, J.P., and Chiang, C.Y.:A Mobile Scaffolding-Aid-Based Bird -Watching Learning System, Proceedings of IEEE International Workshop on Wireless and Mobile Technologies in Education (WMTE'02), pp.15-22, IEEE Computer Society Press, 2002.
- Curtis, M., Luchini, K., Bobrowsky, W., Quintana, C., and Soloway, E.: Handheld Use in K-12: A Descriptive Account, Proceedings of IEEE International Workshop on Wireless and Mobile Technologies in Education (WMTE'02), pp.23-30, IEEE Computer Society Press, 2002.
- Guozhen Zhang; Qun Jin; Shih, T.K. (200). Peer-to-peer based social interaction tools in ubiquitous learning environment, Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2005. Proceedings. 11th International Conference on Volume 1, 20-22 July 2005 Page(s):230 - 236 Vol. 1 (Access restricted).
- Hiroaki Ogata and Yoneo Yano, Context-Aware Support for Computer Supported Ubiquitous Learning, IEEE WMTE2004, pp.27-34, Taiwan, March 23-25, 2004. PDF Preprint.
- Li, L., Zheng, Y., Ogata, H., and Yano, Y.: A conceptual Framework of Computer-Supported Ubiquitous Learning Environment, International Journal of Advanced Technology for Learning.
- Li, L., Zheng, Y., Ogata, H., and Yano, Y.: Ubiquitous Computing in Learning: Toward a Conceptual Framework of Ubiquitous Learning Environment, Int’l J. of Pervasive Comp. and Comm.
- Park, Yeonjeong (2011) A pedagogical framework for mobile learning: Categorizing educational applications of mobile technologies into four types IRRODL,Vol. 12, No. 2. HTML