Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sahar Memar Montazerin, M.D.[2]
Overview[edit | edit source]
Lipoma must be differentiated from liposarcoma, normal adipose tissue, adrenal myelolipoma, angiomyolipoma, and other lipomatous tumors.
Differentiating Lipoma from other Diseases[edit | edit source]
Lipoma must be differentiated from liposarcoma, normal adipose tissue, adrenal myelolipoma, angiomyolipoma, and other lipomatous tumors.
- Lipoma should be differentiated from other lipomatous tumors. Table below compares and describes the characteristics of different lipomatous tumors:
| Lipomatous tumor | Age of onset | Gender preponderance | Location | Clinical features | Pathologic features | Other features | Histologic view |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
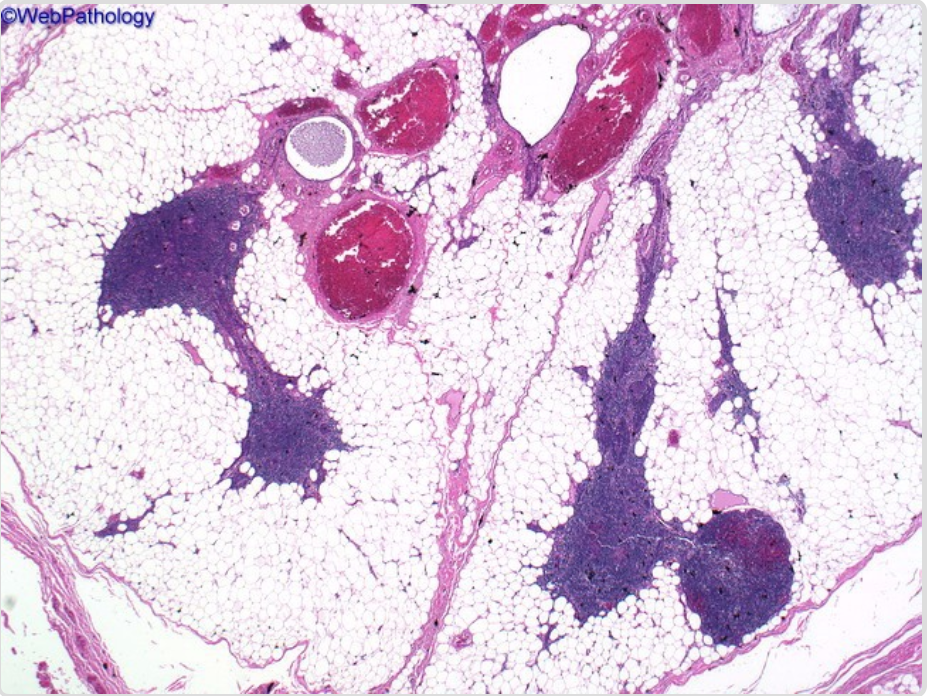
| Angiolipoma[1][2] |
|
|
|
|
|||
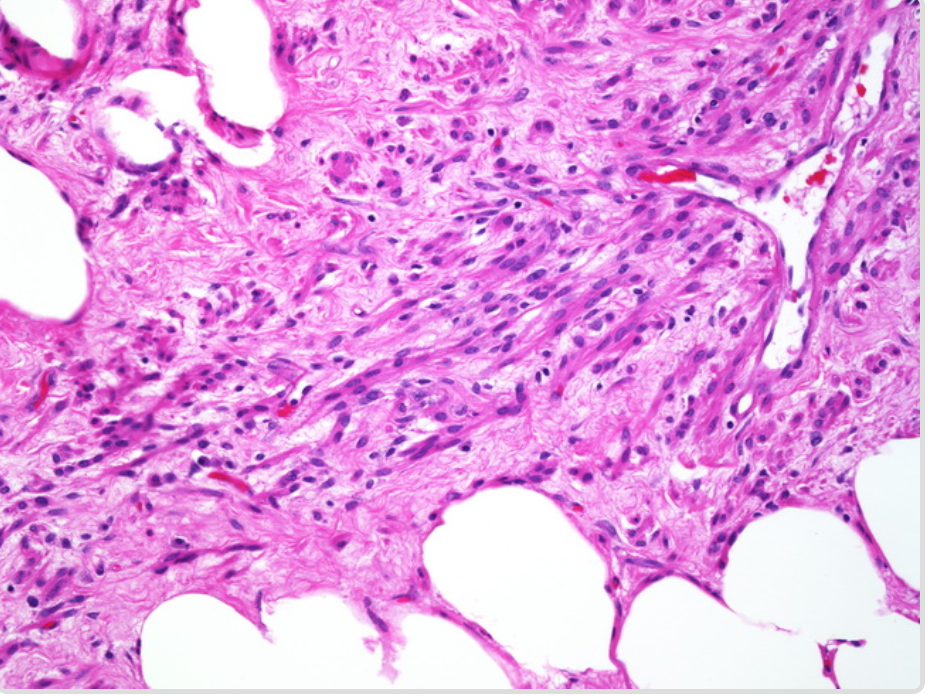
| Myolipoma[4] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
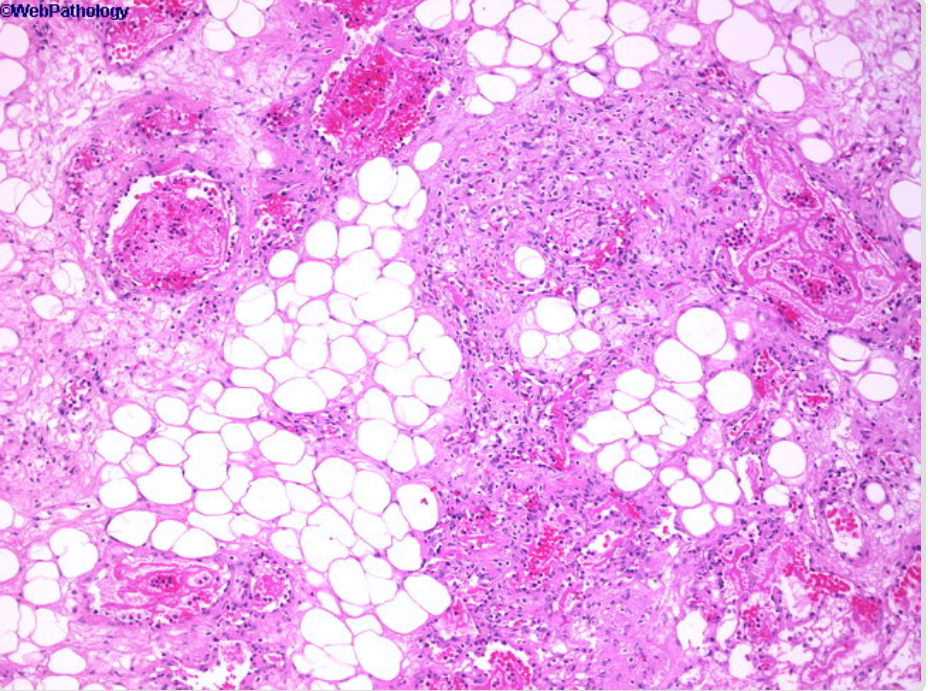
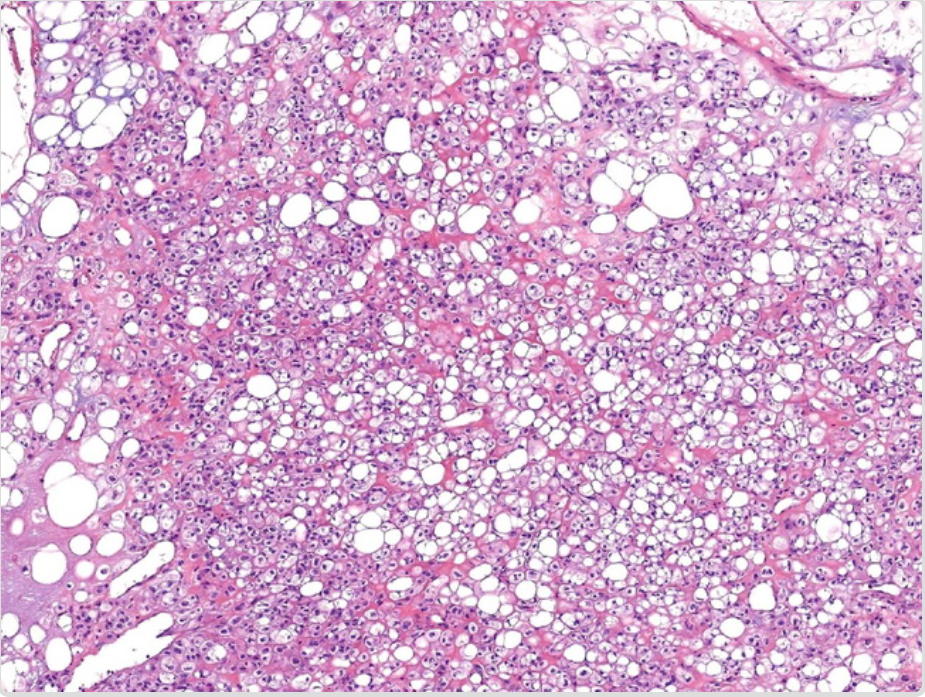
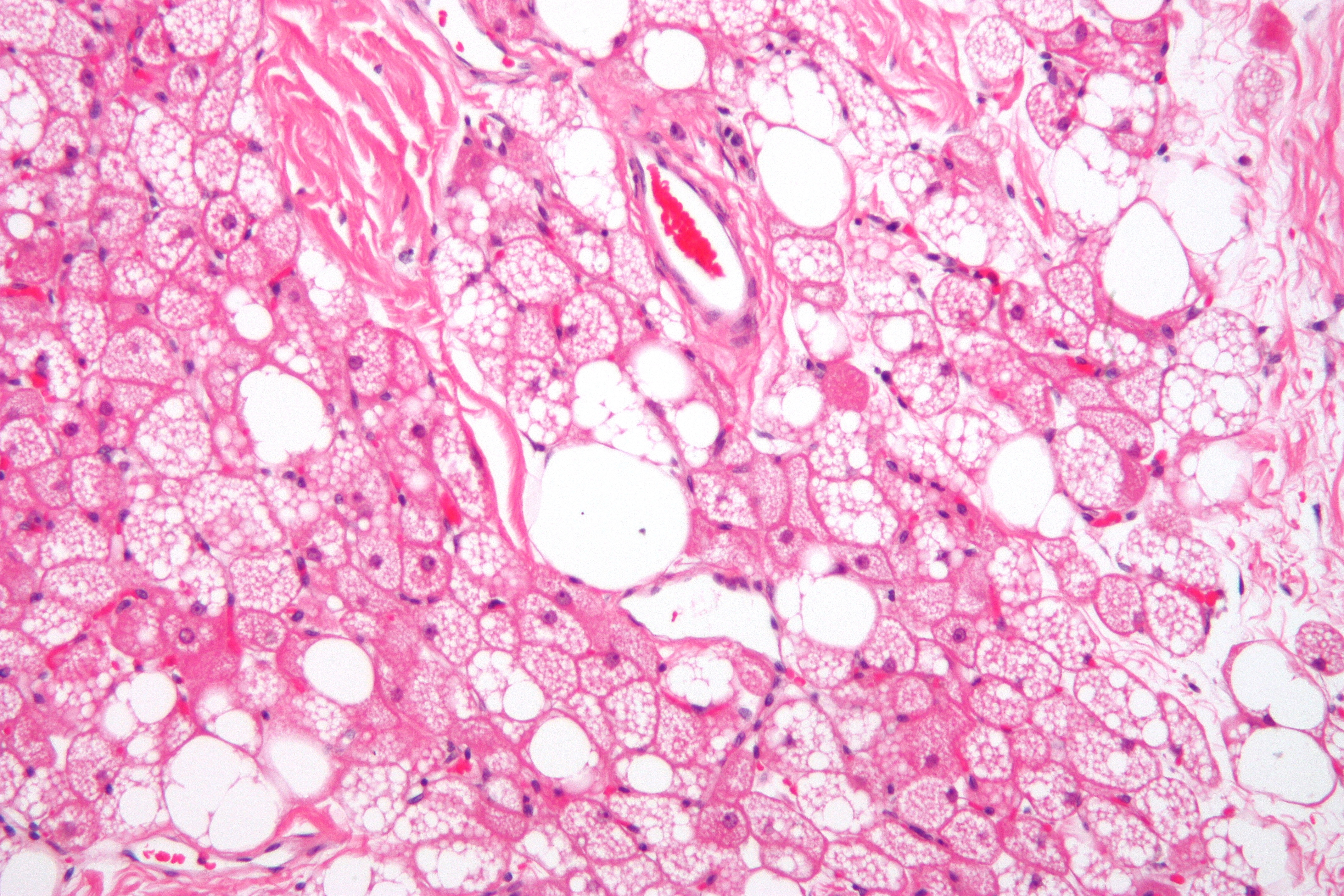
| Myelolipoma[6][7] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
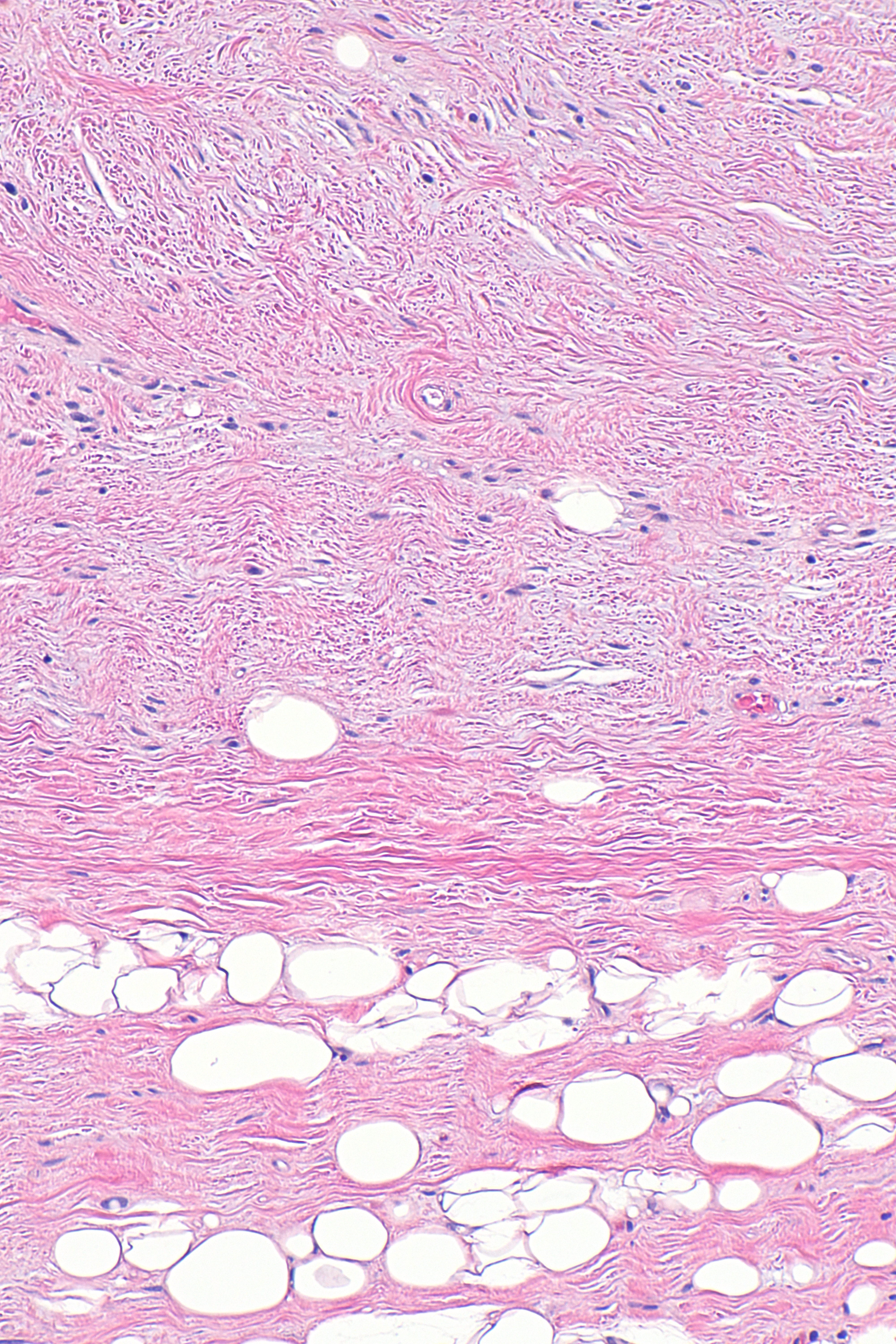
| Spindle Cell/Pleomorphic Lipoma[9] |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Chondroid Lipoma[11] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Hibernoma[13] |
|
|
|
|
|
||
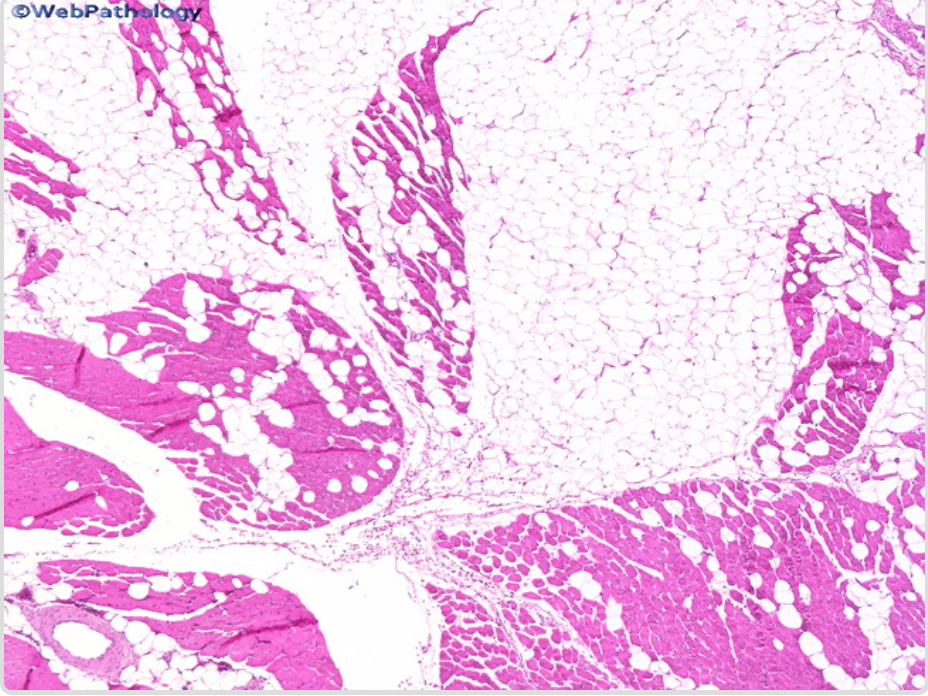
| Intramuscular and Intermuscular Lipomas[15] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
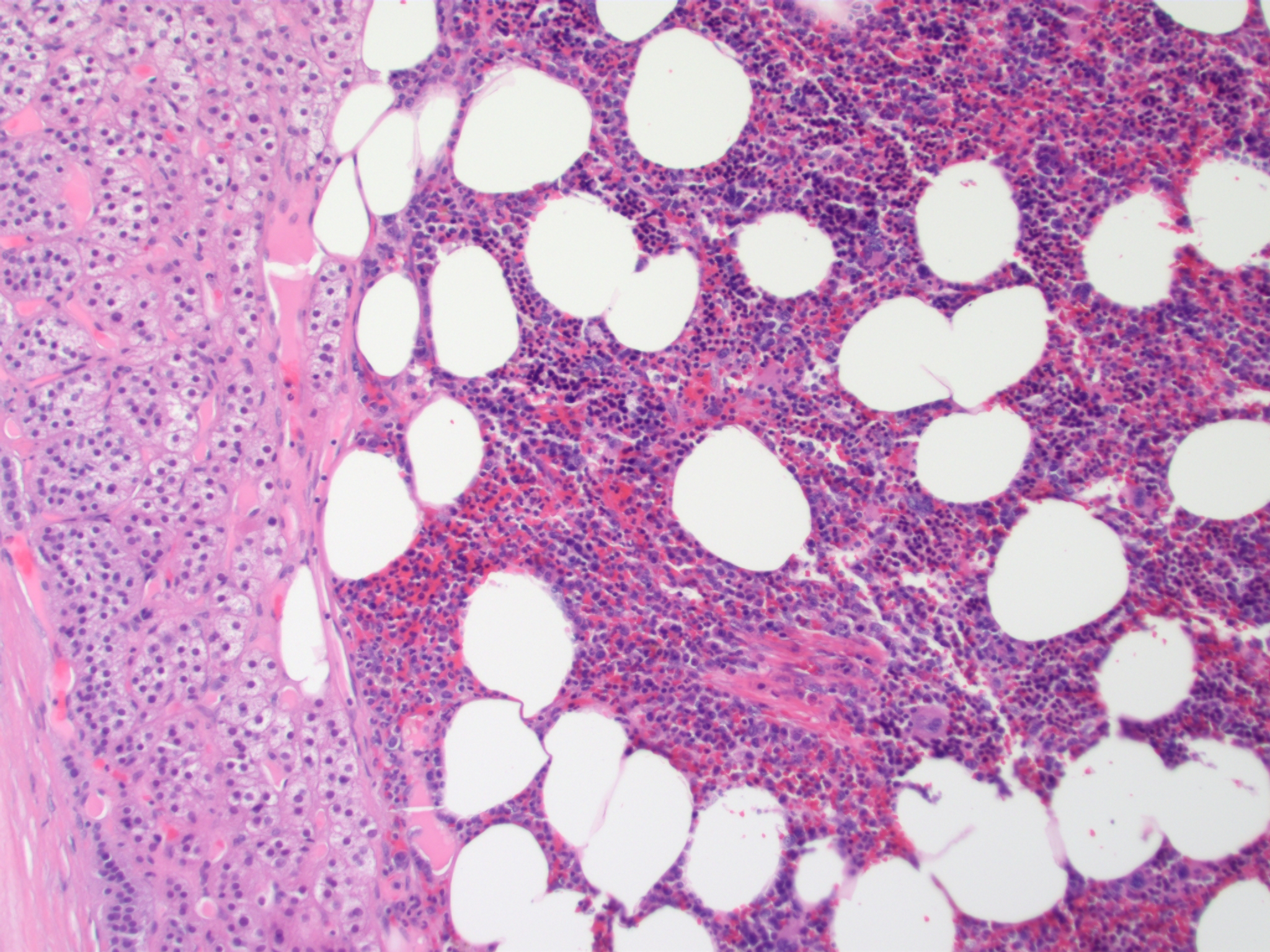
| Thymolipoma[17] |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Lipomas of Tendon Sheaths and Joints[19] |
|
|
|
|
|
_ | |
| Lumbosacral Lipoma[20][21] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
_ |
| Neural Fibrolipoma (Lipofibromatous Hamartoma of Nerves)[22] |
|
|
|
|
|
_ |
In general, there is little differential for a classic lipoma. The main differential is[23]:
- Liposarcoma
- Normal adipose tissue
In certain locations then other fatty masses should be considered :
- Retroperitoneum
- Chest
- Thymolipoma
| Disease | Clinical feature | Laboratory findings | Imaging findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | Weight loss | Abdominal pain | |||
| Retroperitoneal hematoma | _ | _ | ✔ | Anemia | MRI is the best radiologic tool to differentiate between retroperitoneal masses. |
| Retroperitoneal abscess | ✔ | _ | ✔ | Leukocytosis, positive inflammatory markers | |
| Retroperitoneal tumors (.e.g. liposarcoma) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | positive tumor marker | |
| Chronic pancreatitis | _ | ✔ | ✔ | DM type II, amylase and lipase levels may be slightly elevated | |
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Liu, Peng; Che, Wen-Cheng; Ji, Huai-Jun; Jiang, Zhong-Min (2016). "A giant infiltrating angiolipoma of the mediastinum: a case report". Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery. 11 (1). doi:10.1186/s13019-016-0560-6. ISSN 1749-8090.
- ↑ Abbasi NR, Brownell I, Fangman W (January 2007). "Familial multiple angiolipomatosis". Dermatol. Online J. 13 (1): 3. PMID 17511936.
- ↑ Contributed by Dr. Dharam Ramnani in Webpathology
- ↑ Fukushima, Mana; Schaefer, Inga-Marie; Fletcher, Christopher D.M. (2017). "Myolipoma of Soft Tissue". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 41 (2): 153–160. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000737. ISSN 0147-5185.
- ↑ Contributed by Dr. Dharam Ramnani in Webpathology
- ↑ Akamatsu, Hiroki; Koseki, Masato; Nakaba, Hiroyuki; Sunada, Shoji; Ito, Akira; Teramoto, Seiichi; Miyata, Masahiko (2004). "Giant Adrenal Myelolipoma: Report of a Case". Surgery Today. 34 (3): 283–285. doi:10.1007/s00595-003-2682-4. ISSN 0941-1291.
- ↑ Rossi, M.; Ravizza, D.; Fiori, G.; Trovato, C.; Renne, G.; Miller, M.; Tamayo, D.; Crosta, C. (2007). "Thoracic myelolipoma diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasonography and fine-needle aspiration cytology". Endoscopy. 39 (S 1): E114–E115. doi:10.1055/s-2007-966147. ISSN 0013-726X.
- ↑ Contributed by Sarahkayb in Wikimedia commons
- ↑ Shmookler BM, Enzinger FM (January 1981). "Pleomorphic lipoma: a benign tumor simulating liposarcoma. A clinicopathologic analysis of 48 cases". Cancer. 47 (1): 126–33. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<126::aid-cncr2820470121>3.0.co;2-k. PMID 7459800.
- ↑ Contributed by Nephron in Wikimedia commons
- ↑ Gokhale U, Pillai GR, Varghese PV, Samarsinghe D (April 2008). "Chondroid lipoma: a case report". Oman Med J. 23 (2): 116–7. PMC 3282416. PMID 22379550.
- ↑ Contributed by Dr. Dharam Ramnani in Webpathology
- ↑ Furlong, Mary A.; Fanburg–Smith, Julie C.; Miettinen, Markku (2001). "The Morphologic Spectrum of Hibernoma". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 25 (6): 809–814. doi:10.1097/00000478-200106000-00014. ISSN 0147-5185.
- ↑ Contributed by Nephron in Wikimedia commons
- ↑ Nishida, Jun; Morita, Tetsuro; Ogose, Akira; Okada, Kyoji; Kakizaki, Hiroshi; Tajino, Takahiro; Hatori, Masahito; Orui, Hiroshi; Ehara, Shigeru; Satoh, Takashi; Shimamura, Tadashi (2007). "Imaging characteristics of deep-seated lipomatous tumors: intramuscular lipoma, intermuscular lipoma, and lipoma-like liposarcoma". Journal of Orthopaedic Science. 12 (6): 533–541. doi:10.1007/s00776-007-1177-3. ISSN 0949-2658.
- ↑ Contributed by Dr. Dharam Ramnani in Webpathology
- ↑ Guimarães, Marcos D.; Benveniste, Marcelo F.K.; Bitencourt, Almir G.V.; Andrade, Victor P.; Souza, Liliana P.; Gross, Jefferson L.; Godoy, Myrna C.B. (2013). "Thymoma Originating in a Giant Thymolipoma: A Rare Intrathoracic Lesion". The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 96 (3): 1083–1085. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.01.031. ISSN 0003-4975.
- ↑ Contributed by Dr. Dharam Ramnani in Webpathology
- ↑ Gurich RW, Pappas ND (December 2015). "Lipoma of the Tendon Sheath in the Fourth Extensor Compartment of the Hand". Am J. Orthop. 44 (12): 561–2. PMID 26665243.
- ↑ Kang, Hyun-Seung; Wang, Kyu-Chang; Kim, Kwang Myung; Kim, Seung Ki; Cho, Byung Kyu (2006). "Prognostic factors affecting urologic outcome after untethering surgery for lumbosacral lipoma". Child's Nervous System. 22 (9): 1111–1121. doi:10.1007/s00381-006-0088-5. ISSN 0256-7040.
- ↑ Jones, Victoria; Wykes, Victoria; Cohen, Nicki; Thompson, Dominic; Jacques, Tom S (2018). "The pathology of lumbosacral lipomas: macroscopic and microscopic disparity have implications for embryogenesis and mode of clinical deterioration". Histopathology. 72 (7): 1136–1144. doi:10.1111/his.13469. ISSN 0309-0167.
- ↑ Al-Jabri T, Garg S, Mani GV (September 2010). "Lipofibromatous hamartoma of the median nerve". J Orthop Surg Res. 5: 71. doi:10.1186/1749-799X-5-71. PMC 2955673. PMID 20920178.
- ↑ Lipoma.Dr Ahmed Abd Rabou and Dr Frank Gaillard, et al. Radiopaedia.org 2015.http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lipoma
- ↑ Khin Thway, Rashpal Flora, Chirag Shah, David Olmos & Cyril Fisher (2012). "Diagnostic utility of p16, CDK4, and MDM2 as an immunohistochemical panel in distinguishing well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas from other adipocytic tumors". The American journal of surgical pathology. 36 (3): 462–469. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182417330. PMID 22301498. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ J. Rosai, M. Akerman, P. Dal Cin, I. DeWever, C. D. Fletcher, N. Mandahl, F. Mertens, F. Mitelman, A. Rydholm, R. Sciot, G. Tallini, H. Van den Berghe, W. Van de Ven, R. Vanni & H. Willen (1996). "Combined morphologic and karyotypic study of 59 atypical lipomatous tumors. Evaluation of their relationship and differential diagnosis with other adipose tissue tumors (a report of the CHAMP Study Group)". The American journal of surgical pathology. 20 (10): 1182–1189. PMID 8827023. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Dal Cin, Paola; Kools, Patrick; Sciot, Raf; De Wever, Ivo; Van Damme, Boudewijn; Van de Ven, Wim; Van Den Berghe, Herman (1993). "Cytogenetic and fluorescence in situ hybridization investigation of ring chromosomes characterizing a specific pathologic subgroup of adipose tissue tumors". Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics. 68 (2): 85–90. doi:10.1016/0165-4608(93)90001-3. ISSN 0165-4608.
- ↑ Dei Tos, Angelo P.; Doglioni, Claudio; Piccinin, Sara; Sciot, Raf; Furlanetto, Alberto; Boiocchi, Mauro; Dal Cin, Paola; Maestro, Roberta; Fletcher, Christopher D. M.; Tallini, Giovanni (2000). "Coordinated expression and amplification of theMDM2,CDK4, andHMGI-C genes in atypical lipomatous tumours". The Journal of Pathology. 190 (5): 531–536. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(200004)190:5<531::AID-PATH579>3.0.CO;2-W. ISSN 0022-3417.
- ↑ Dei Tos, A (2000). "Liposarcoma: New entities and evolving concepts". Annals of Diagnostic Pathology. 4 (4): 252–266. doi:10.1053/adpa.2000.8133. ISSN 1092-9134.
- ↑ M. D. Kraus, L. Guillou & C. D. Fletcher (1997). "Well-differentiated inflammatory liposarcoma: an uncommon and easily overlooked variant of a common sarcoma". The American journal of surgical pathology. 21 (5): 518–527. PMID 9158675. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ P. Argani, F. Facchetti, G. Inghirami & J. Rosai (1997). "Lymphocyte-rich well-differentiated liposarcoma: report of nine cases". The American journal of surgical pathology. 21 (8): 884–895. PMID 9255251. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ H. L. Evans (1979). "Liposarcoma: a study of 55 cases with a reassessment of its classification". The American journal of surgical pathology. 3 (6): 507–523. PMID 534388. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ A. P. Dei Tos, T. Mentzel, P. L. Newman & C. D. Fletcher (1994). "Spindle cell liposarcoma, a hitherto unrecognized variant of liposarcoma. Analysis of six cases". The American journal of surgical pathology. 18 (9): 913–921. PMID 8067512. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ D. C. Dahlin, K. K. Unni & T. Matsuno (1977). "Malignant (fibrous) histiocytoma of bone--fact or fancy?". Cancer. 39 (4): 1508–1516. PMID 192432. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Rodriguez, Fausto J.; Folpe, Andrew L.; Giannini, Caterina; Perry, Arie (2012). "Pathology of peripheral nerve sheath tumors: diagnostic overview and update on selected diagnostic problems". Acta Neuropathologica. 123 (3): 295–319. doi:10.1007/s00401-012-0954-z. ISSN 0001-6322.
- ↑ Choi, Kwangmin; Komurov, Kakajan; Fletcher, Jonathan S.; Jousma, Edwin; Cancelas, Jose A.; Wu, Jianqiang; Ratner, Nancy (2017). "An inflammatory gene signature distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and macrophages from cells in the normal peripheral nervous system". Scientific Reports. 7 (1). doi:10.1038/srep43315. ISSN 2045-2322.
- ↑ Liao, Chung-Ping; Booker, Reid C.; Brosseau, Jean-Philippe; Chen, Zhiguo; Mo, Juan; Tchegnon, Edem; Wang, Yong; Clapp, D. Wade; Le, Lu Q. (2018). "Contributions of inflammation and tumor microenvironment to neurofibroma tumorigenesis". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 128 (7): 2848–2861. doi:10.1172/JCI99424. ISSN 0021-9738.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 Staser, K.; Yang, F.-C.; Clapp, D. W. (2010). "Mast cells and the neurofibroma microenvironment". Blood. 116 (2): 157–164. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-09-242875. ISSN 0006-4971.
- ↑ Muir, David; Neubauer, Debbie; Lim, Ingrid T.; Yachnis, Anthony T.; Wallace, Margaret R. (2001). "Tumorigenic Properties of Neurofibromin-Deficient Neurofibroma Schwann Cells". The American Journal of Pathology. 158 (2): 501–513. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63992-2. ISSN 0002-9440.
- ↑ Wilkinson, Lana M.; Manson, David; Smith, Charles R. (2004). "Best Cases from the AFIP". RadioGraphics. 24 (suppl_1): S237–S242. doi:10.1148/rg.24si035170. ISSN 0271-5333.
- ↑ Bernthal, Nicholas; Jones, Kevin; Monument, Michael; Liu, Ting; Viskochil, David; Randall, R. (2013). "Lost in Translation: Ambiguity in Nerve Sheath Tumor Nomenclature and Its Resultant Treatment Effect". Cancers. 5 (4): 519–528. doi:10.3390/cancers5020519. ISSN 2072-6694.
- ↑ Mautner, V. F.; Friedrich, R. E.; von Deimling, A.; Hagel, C.; Korf, B.; Knöfel, M. T.; Wenzel, R.; Fünsterer, C. (2003). "Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in neurofibromatosis type 1: MRI supports the diagnosis of malignant plexiform neurofibroma". Neuroradiology. 45 (9): 618–625. doi:10.1007/s00234-003-0964-6. ISSN 0028-3940.
- ↑ Shen, M H; Harper, P S; Upadhyaya, M (1996). "Molecular genetics of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)". Journal of Medical Genetics. 33 (1): 2–17. doi:10.1136/jmg.33.1.2. ISSN 1468-6244.
- ↑ Rubin, Joshua B.; Gutmann, David H. (2005). "Neurofibromatosis type 1 — a model for nervous system tumour formation?". Nature Reviews Cancer. 5 (7): 557–564. doi:10.1038/nrc1653. ISSN 1474-175X.
- ↑ Gray, Mark H. (1990). "Immunohistochemical Demonstration of Factor XIIIa Expression in Neurofibromas". Archives of Dermatology. 126 (4): 472. doi:10.1001/archderm.1990.01670280056009. ISSN 0003-987X.
- ↑ Schwannoma. Dr Tim Luijkx and Dr Sara Wein et al. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/schwannoma
- ↑ Vestibular Schwannoma. Wikipedia(2015) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vestibular_schwannoma Accessed on October 2 2015
- ↑ Giordano J, Rogers LV (1989). "Peripherally administered serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists reduce inflammatory pain in rats". European Journal of Pharmacology. 170 (1–2): 83–6. PMID 2612565.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ Kolvenbach H, Lauven PM, Schneider B, Kunath U (1989). "Repetitive intercostal nerve block via catheter for postoperative pain relief after thoracotomy". The Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgeon. 37 (5): 273–6. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1020331. PMID 2588243. Retrieved 2015-11-20.
- ↑ Opaleva-Stegantseva VA, Ivanov AG, Gavrilina IA, Khar'kov EI, Ratovskaia VI (1986). "[Incidence of sudden death cases in acute coronary insufficiency and acute myocardial infarction at the pre-hospital stage in Krasnoyarsk]". Kardiologiia (in Russian). 26 (5): 23–6. PMID 3735913.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ Misago N, Inoue T, Narisawa Y (2007). "Unusual benign myxoid nerve sheath lesion: myxoid palisaded encapsulated neuroma (PEN) or nerve sheath myxoma with PEN/PEN-like features?". Am J Dermatopathol. 29 (2): 160–4. doi:10.1097/01.dad.0000256688.91974.09. PMID 17414438.
- ↑ Lee EJ, Calcaterra TC, Zuckerbraun L (1998). "Traumatic neuromas of the head and neck". Ear Nose Throat J. 77 (8): 670–4, 676. PMID 9745184.
- ↑ Hanna SA, Catapano J, Borschel GH (2016). "Painful pediatric traumatic neuroma: surgical management and clinical outcomes". Childs Nerv Syst. 32 (7): 1191–4. doi:10.1007/s00381-016-3109-z. PMID 27179535.
- ↑ Foltán R, Klíma K, Spacková J, Sedý J (2008). "Mechanism of traumatic neuroma development". Med Hypotheses. 71 (4): 572–6. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2008.05.010. PMID 18599222.
- ↑ Yao C, Zhou X, Zhao B, Sun C, Poonit K, Yan H (2017). "Treatments of traumatic neuropathic pain: a systematic review". Oncotarget. 8 (34): 57670–57679. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16917. PMC 5593675. PMID 28915703.
- ↑ Gray MH, Smoller BR, McNutt NS, Hsu A (1990). "Neurofibromas and neurotized melanocytic nevi are immunohistochemically distinct neoplasms". Am J Dermatopathol. 12 (3): 234–41. PMID 1693815.
- ↑ Chen Y, Klonowski PW, Lind AC, Lu D (2012). "Differentiating neurotized melanocytic nevi from neurofibromas using Melan-A (MART-1) immunohistochemical stain". Arch Pathol Lab Med. 136 (7): 810–5. doi:10.5858/arpa.2011-0335-OA. PMID 22742554.
- ↑ Singh N, Chandrashekar L, Kar R, Sylvia MT, Thappa DM (2015). "Neurotized congenital melanocytic nevus resembling a pigmented neurofibroma". Indian J Dermatol. 60 (1): 46–50. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.147789. PMC 4318062. PMID 25657396.
- ↑ Gray MH, Smoller BR, McNutt NS, Hsu A (1990). "Immunohistochemical demonstration of factor XIIIa expression in neurofibromas. A practical means of differentiating these tumors from neurotized melanocytic nevi and schwannomas". Arch Dermatol. 126 (4): 472–6. PMID 1690969.
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/cutaneous-myxoma
- ↑ Alaiti, Samer; Nelson, Fern P.; Ryoo, Jei W. (2000). "Solitary cutaneous myxoma". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 43 (2): 377–379. doi:10.1067/mjd.2000.101878. ISSN 0190-9622.
- ↑ Carney, J. Aidan (1986). "Cutaneous Myxomas". Archives of Dermatology. 122 (7): 790. doi:10.1001/archderm.1986.01660190068018. ISSN 0003-987X.
- ↑ Iida, Ken; Egi, Takeshi; Shigi, Masato; Sogabe, Yusuke; Ohashi, Hirotsugu (2019). "Cutaneous Myxoma of Multiple Lesions". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open. 7 (2): e2040. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002040. ISSN 2169-7574.
- ↑ Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Miettinen M (2005). "Nerve sheath myxoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 57 morphologically distinctive, S-100 protein- and GFAP-positive, myxoid peripheral nerve sheath tumors with a predilection for the extremities and a high local recurrence rate". Am J Surg Pathol. 29 (12): 1615–24. PMID 16327434.
- ↑ Yadav SK, Singh S, Sarin N, Naeem R, Pruthi SK (2019). "Nerve Sheath Myxoma of Scalp: A Rare Site of Presentation". Int J Trichology. 11 (1): 34–37. doi:10.4103/ijt.ijt_45_18. PMC 6385516. PMID 30820132.
- ↑ Bhat A, Narasimha A, C V, Vk S (2015). "Nerve sheath myxoma: report of a rare case". J Clin Diagn Res. 9 (4): ED07–9. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2015/10911.5810. PMC 4437072. PMID 26023558.
- ↑ Avninder S, Ramesh V, Vermani S (2007). "Benign nerve sheath myxoma (myxoid neurothekeoma) in the leg". Dermatol Online J. 13 (2): 14. PMID 17498433.
- ↑ Kim BW, Won CH, Chang SE, Lee MW (2014). "A case of nerve sheath myxoma on finger". Indian J Dermatol. 59 (1): 99–101. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.123526. PMC 3884944. PMID 24470676.
- ↑ Pulitzer DR, Reed RJ (1985). "Nerve-sheath myxoma (perineurial myxoma)". Am J Dermatopathol. 7 (5): 409–21. PMID 4091218.
- ↑ Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Ismaili, N.; Bastuji-Garin, S.; Zeller, J.; Wechsler, J.; Revuz, J.; Wolkenstein, P. (2005). "Symptoms associated with malignancy of peripheral nerve sheath tumours: a retrospective study of 69 patients with neurofibromatosis 1". British Journal of Dermatology. 153 (1): 79–82. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06558.x. ISSN 0007-0963.
- ↑ Evans DG, Baser ME, McGaughran J, Sharif S, Howard E, Moran A (2002). "Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in neurofibromatosis 1". J Med Genet. 39 (5): 311–4. PMC 1735122. PMID 12011145.
- ↑ Panigrahi S, Mishra SS, Das S, Dhir MK (2013). "Primary malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor at unusual location". J Neurosci Rural Pract. 4 (Suppl 1): S83–6. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.116480. PMC 3808069. PMID 24174807.
- ↑ Ferrari A, Bisogno G, Carli M (2007). "Management of childhood malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor". Paediatr Drugs. 9 (4): 239–48. doi:10.2165/00148581-200709040-00005. PMID 17705563.
- ↑ Neville H, Corpron C, Blakely ML, Andrassy R (2003). "Pediatric neurofibrosarcoma". J Pediatr Surg. 38 (3): 343–6, discussion 343-6. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2003.50105. PMID 12632346.
- ↑ Zehou, Ouidad; Fabre, Elizabeth; Zelek, Laurent; Sbidian, Emilie; Ortonne, Nicolas; Banu, Eugeniu; Wolkenstein, Pierre; Valeyrie-Allanore, Laurence (2013). "Chemotherapy for the treatment of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors in neurofibromatosis 1: a 10-year institutional review". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 8 (1): 127. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-127. ISSN 1750-1172.
- ↑ Vasiliadis, K.; Papavasiliou, C.; Fachiridis, D.; Pervana, S.; Michaelides, M.; Kiranou, M.; Makridis, C. (2012). "Retroperitoneal extra-adrenal ganglioneuroma involving the infrahepatic inferior vena cava, celiac axis and superior mesenteric artery: A case report". International Journal of Surgery Case Reports. 3 (11): 541–543. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.07.008. ISSN 2210-2612.
- ↑ https://radiopaedia.org/articles/ganglioneuroma
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 Coffin CM, Watterson J, Priest JR, Dehner LP (1995). "Extrapulmonary inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (inflammatory pseudotumor). A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 84 cases". Am J Surg Pathol. 19 (8): 859–72. PMID 7611533.
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 78.2 78.3 Wenig BM, Devaney K, Bisceglia M (1995). "Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the larynx. A clinicopathologic study of eight cases simulating a malignant spindle cell neoplasm". Cancer. 76 (11): 2217–29. PMID 8635024.
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 Ramachandra S, Hollowood K, Bisceglia M, Fletcher CD (1995). "Inflammatory pseudotumour of soft tissues: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis of 18 cases". Histopathology. 27 (4): 313–23. PMID 8847061.
- ↑ 80.0 80.1 Häusler M, Schaade L, Ramaekers VT, Doenges M, Heimann G, Sellhaus B (2003). "Inflammatory pseudotumors of the central nervous system: report of 3 cases and a literature review". Hum Pathol. 34 (3): 253–62. doi:10.1053/hupa.2003.35. PMID 12673560.
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 81.2 81.3 Rabban JT, Zaloudek CJ, Shekitka KM, Tavassoli FA (2005). "Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the uterus: a clinicopathologic study of 6 cases emphasizing distinction from aggressive mesenchymal tumors". Am J Surg Pathol. 29 (10): 1348–55. PMID 16160478.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 Kovach SJ, Fischer AC, Katzman PJ, Salloum RM, Ettinghausen SE, Madeb R; et al. (2006). "Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors". J Surg Oncol. 94 (5): 385–91. doi:10.1002/jso.20516. PMID 16967468.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 Coffin CM, Dehner LP, Meis-Kindblom JM (1998). "Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, inflammatory fibrosarcoma, and related lesions: an historical review with differential diagnostic considerations". Semin Diagn Pathol. 15 (2): 102–10. PMID 9606802.
- ↑ 84.0 84.1 Berardi RS, Lee SS, Chen HP, Stines GJ (1983). "Inflammatory pseudotumors of the lung". Surg Gynecol Obstet. 156 (1): 89–96. PMID 6336632.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 Coffin CM, Hornick JL, Fletcher CD (2007). "Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor: comparison of clinicopathologic, histologic, and immunohistochemical features including ALK expression in atypical and aggressive cases". Am J Surg Pathol. 31 (4): 509–20. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000213393.57322.c7. PMID 17414097.
- ↑ Cukic O, Jovanovic MB (2019). "Large Fibroepithelial Polyp of the Palatine Tonsil". Ear Nose Throat J: 145561319841203. doi:10.1177/0145561319841203. PMID 30997841.
- ↑ Vatansever M, Dinç E, Dursun Ö, Oktay ÖÖ, Arpaci R (2019). "Atypical presentation of fibroepithelial polyp: a report of two cases". Arq Bras Oftalmol. doi:10.5935/0004-2749.20190050. PMID 30916216.
- ↑ Rexhepi M, Trajkovska E, Besimi F, Rufati N (2018). "Giant Fibroepithelial Polyp of Vulva: A Case Report and Review of Literature". Pril (Makedon Akad Nauk Umet Odd Med Nauki). 39 (2–3): 127–130. doi:10.2478/prilozi-2018-0051. PMID 30864355.
- ↑ Jabbour J, Chappell JR, Busby M, McCubbery NW, Brown DF, Park SJK; et al. (2019). "Glottic Obstruction from Fibroepithelial Polyp". Am J Case Rep. 20: 219–223. doi:10.12659/AJCR.914907. PMC 6388646. PMID 30778021.
- ↑ Hong P, Cai Y, Li Z, Fan S, Yang K, Hao H; et al. (2019). "Modified Laparoscopic Partial Ureterectomy for Adult Ureteral Fibroepithelial Polyp: Technique and Initial Experience". Urol Int. 102 (1): 13–19. doi:10.1159/000494804. PMID 30448831.
- ↑ Uçar M, Baş E, Akkoç A, Topçuoğlu M (2018). "Fibroepithelial Polyp of the Ureter: A Rare Cause of Hydronephrosis". J Endourol Case Rep. 4 (1): 166–168. doi:10.1089/cren.2018.0031. PMC 6225073. PMID 30426076.
- ↑ Chaker K, Rhouma SB, Daly KM, Zehani A, Bibi M, Chehida MAB; et al. (2019). "Benign fibroepithelial polyp of the ureter: A case report". Urol Case Rep. 22: 52–53. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.10.019. PMC 6226574. PMID 30425926.
- ↑ Hajji F, Moufid K, Ghoundale O, Touiti D (2019). "A rare case of successful endoscopic management of a fibroepithelial polyp with intussusception of the ureter and periodic prolapse into bladder". Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 101 (2): e66–e70. doi:10.1308/rcsann.2018.0198. PMC 6351868. PMID 30421620.
- ↑ Lee H, Sade I, Gilani S, Zhong M, Lombardo G (2018). "A Giant Fibroepithelial Polyp of the Small Bowel Associated with High-Grade Obstruction". Am Surg. 84 (7): e210–e211. PMID 30401014.
- ↑ Chaker K (2019). "Benign fibroepithelial polyp of the ureter: A case report". Urol Case Rep. 22: 15–16. doi:10.1016/j.eucr.2018.09.021. PMC 6180234. PMID 30319938.
- ↑ Lozano-Peña AK, Lamadrid-Zertuche AC, Ocampo-Candiani J (2019). "Giant fibroepithelial polyp of the vulva". Australas J Dermatol. 60 (1): 70–71. doi:10.1111/ajd.12886. PMID 30009441.
- ↑ Eckstein M, Agaimy A, Woenckhaus J, Winter A, Bittmann I, Janzen J; et al. (2019). "DICER1 mutation-positive giant botryoid fibroepithelial polyp of the urinary bladder mimicking embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma". Hum Pathol. 84: 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2018.05.015. PMID 29883781.
- ↑ Akdere H, Çevik G (2018). "Rare Fibroepithelial Polyp Extending Along the Ureter: A Case Report". Balkan Med J. 35 (3): 275–277. doi:10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.1537. PMC 5981127. PMID 29843497.
- ↑ Ballard DH, Rove KO, Coplen DE, Chen TY, Hulett Bowling RL (2018). "Fibroepithelial polyp causing urethral obstruction: Diagnosis by cystourethrogram". Clin Imaging. 51: 164–167. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2018.05.009. PMC 6404776. PMID 29800931.
- ↑ Amin A, Amin Z, Al Farsi AR (2018). "Septic presentation of a giant fibroepithelial polyp of the vulva". BMJ Case Rep. 2018. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222789. PMID 29574427.
- ↑ Gupta R, Smita S, Sinha R, Sinha N, Sinha L (2018). "Giant fibroepithelial polyp of the thigh and retroperitoneal fibromatosis in a young woman: a rare case". Skeletal Radiol. 47 (9): 1299–1304. doi:10.1007/s00256-018-2904-x. PMID 29487969.
- ↑ Rajeesh Mohammed PK, Choudhury BK, Dalai RP, Rana V (2017). "Fibroepithelial Polyp with Sebaceous Hyperplasia: A Case Report". Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 38 (3): 404–406. doi:10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_124_17. PMC 5686997. PMID 29200704.
- ↑ Lee MH, Hwang JY, Lee JH, Kim DH, Song SH (2017). "Fibroepithelial polyp of the vulva accompanied by lymphangioma circumscriptum". Obstet Gynecol Sci. 60 (4): 401–404. doi:10.5468/ogs.2017.60.4.401. PMC 5547092. PMID 28791276.
- ↑ Ten Donkelaar CS, Houwert AC, Ten Kate FJW, Lock MTWT (2017). "Polypoid arteriovenous malformation of the ureter mimicking a fibroepithelial polyp, a case report". BMC Urol. 17 (1): 55. doi:10.1186/s12894-017-0237-z. PMC 5504856. PMID 28693464.
- ↑ Saito N, Yamasaki M, Daido W, Ishiyama S, Deguchi N, Taniwaki M (2017). "A bronchial fibroepithelial polyp with abnormal findings on auto-fluorescence imaging". Respirol Case Rep. 5 (5): e00244. doi:10.1002/rcr2.244. PMC 5465754. PMID 28603622.