 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Trusopt, others |
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Topical (eye drops) |
| Defined daily dose | 0.3 ml[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602022 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | ~33% |
| Elimination half-life | 4 months |
| Chemical and physical data | |
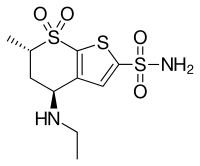
| Formula | C10H16N2O4S3 |
| Molar mass | 324.43 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dorzolamide, sold under the brand name Trusopt among others, is medications used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma.[2] It is used as an eye drop.[2] Effects begin within three hours and lasts for at least eight hours.[2] It is also available as the combination dorzolamide/timolol.[2]
Common side effects include eye discomfort, eye redness, taste changes, and blurry vision.[2] Serious side effects include Steven Johnson syndrome.[2] Those allergic to sulfonamides may be allergic to dorzolamide.[2][3] Use is not recommended in pregnancy or breastfeeding.[3] It is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and works by decreasing the production of aqueous humour.[2]
Dorzolamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1994.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[3] A 5 milliliter bottle in the United Kingdom costs the NHS less than £2 as of 2019.[3] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$7.10.[4] In 2017, it was the 281st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[5][6]
Medical uses[edit | edit source]
Dorzolamide hydrochloride is used to lower excessive intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
Dosage[edit | edit source]
The defined daily dose is 0.3 ml.[1]
Side effects[edit | edit source]
Ocular stinging, burning, itching and bitter taste.[7] It causes shallowing of the anterior chamber and leads to transient myopia.
Pharmacodynamics[edit | edit source]
It lowers IOP by about 20%.[7] Carbonic Anhydrase can convert H2CO3 into HCO3 (bicarbonate) and H+. The H+ is then exchanged for sodium (Na) which allows you to make aqueous humor. By blocking carbonic anhydrase, the Na/H exchanger can't work, which will decrease Na in the cell and prevent aqueous humor production.
History[edit | edit source]
This drug, developed by Merck, was the first drug in human therapy (market introduction 1995) that resulted from structure-based drug design. It was developed to circumvent the systemic side effects of acetazolamide which has to be taken orally.[7]
Society and culture[edit | edit source]
Cost[edit | edit source]
A 5 milliliter bottle in the United Kingdom costs the NHS less than £2 as of 2019.[3] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$7.10.[4] In 2017, it was the 281st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than one million prescriptions.[5][6]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 24 August 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 "Dorzolamide Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 27 March 2019. Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 1148. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 12 February 2021. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Dorzolamide Hydrochloride - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 23 May 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 KD Tripari MD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology (5th ed.). Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers(P) Ltd. p. 88. ISBN 81-8061-187-6.
Further reading[edit | edit source]
- Kubinyi H (1999). "Chance favors the prepared mind--from serendipity to rational drug design". J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 19 (1–4): 15–39. doi:10.3109/10799899909036635. PMID 10071748.
- Plummer C, MacKay E, Gelatt K (2006). "Comparison of the effects of topical administration of a fixed combination of dorzolamide-timolol to monotherapy with timolol or dorzolamide on IOP, pupil size, and heart rate in glaucomatous dogs". Vet Ophthalmol. 9 (4): 245–9. doi:10.1111/j.1463-5224.2006.00469.x. PMID 16771760.
- Grover S, Apushkin M, Fishman G (2006). "Topical dorzolamide for the treatment of cystoid macular edema in patients with retinitis pigmentosa". Am J Ophthalmol. 141 (5): 850–8. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2005.12.030. PMID 16546110.
- Almeida G, Faria e Souza S (2006). "Effect of topical dorzolamide on rabbit central corneal thickness". Braz J Med Biol Res. 39 (2): 277–81. doi:10.1590/S0100-879X2006000200015. PMID 16470316.
== External links ==
| Identifiers: |
|
|---|
.svg.png)
.svg.png)